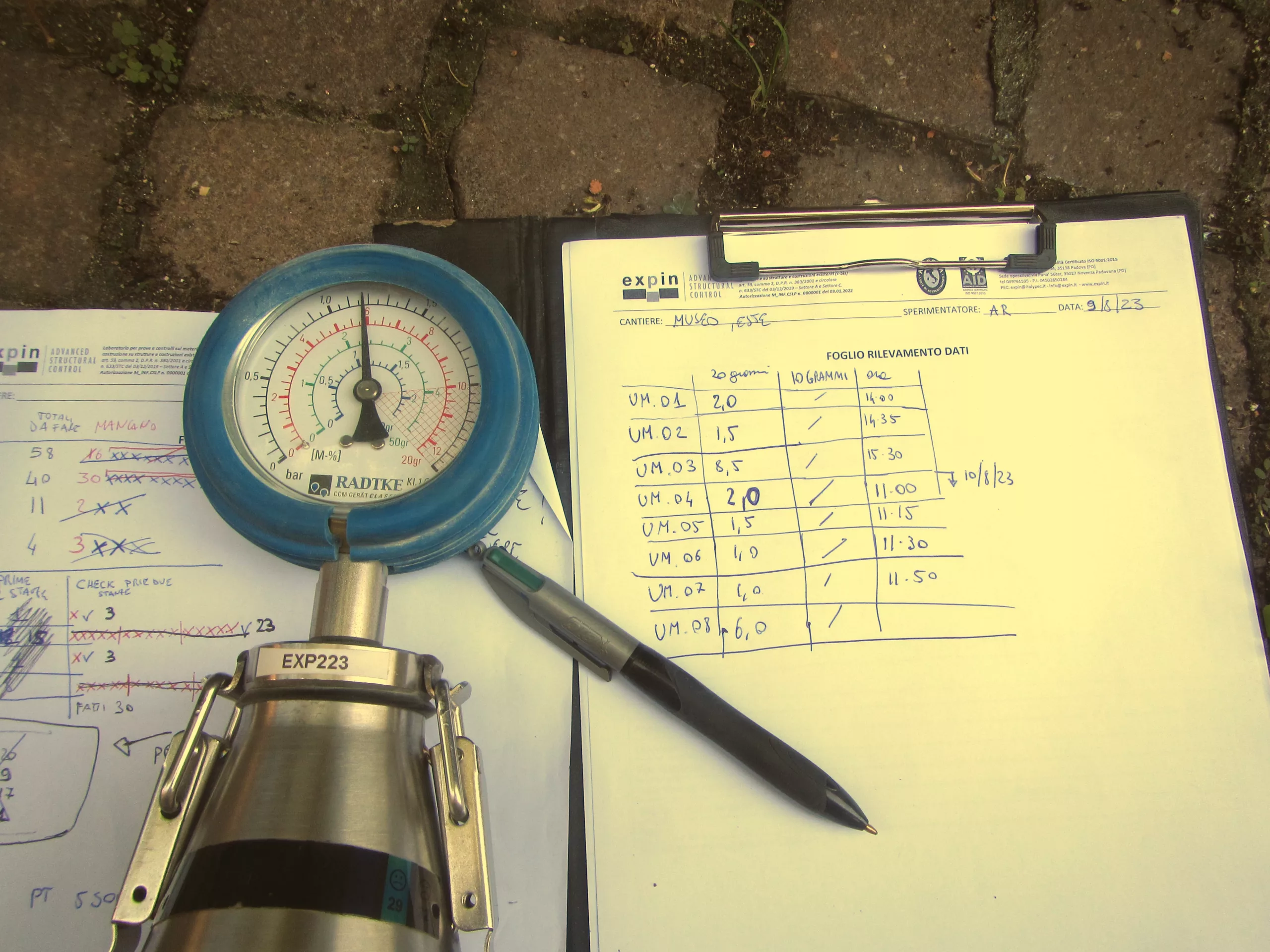


Estimation of moisture content in mortar through carbide method
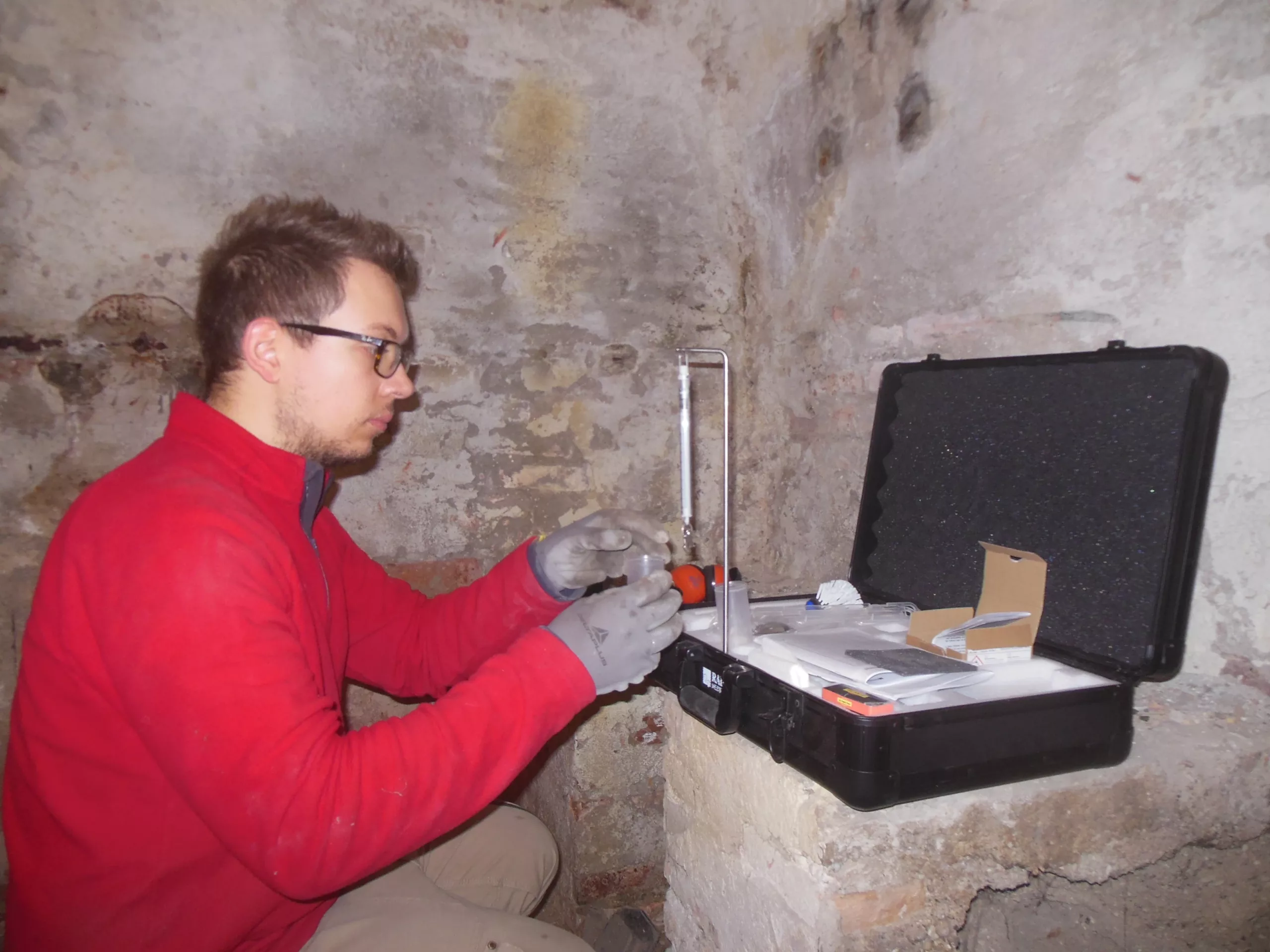
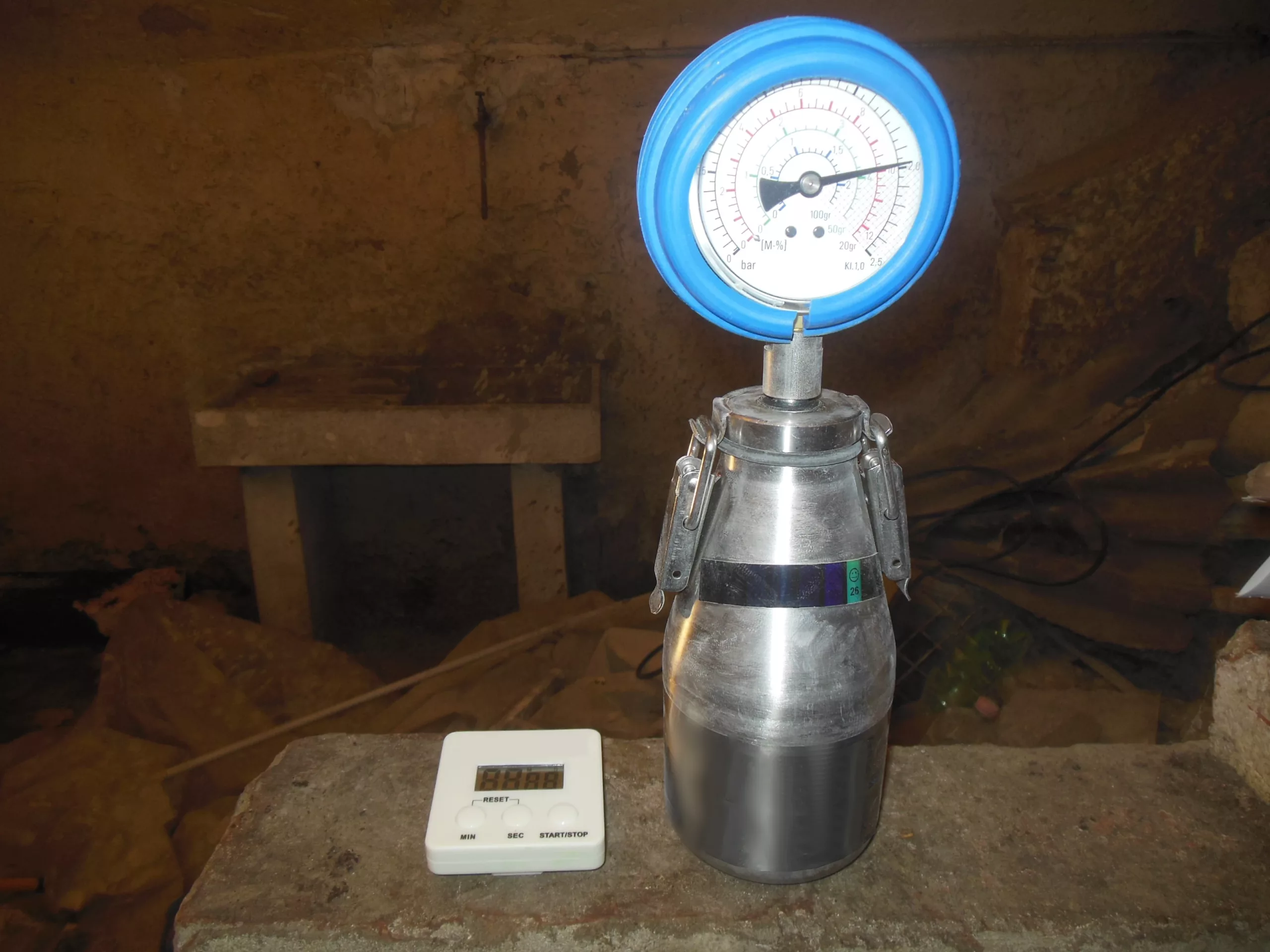
The carbide method allows the moisture content of building materials (concrete, mortar, masonry, …) to be estimated on site using the calcium carbide reaction method. The carbide hygrometer consists of a sealed chamber in which the sampled material, properly prepared and weighed, is placed, together with a known quantity of calcium carbide (CaC2). The calcium carbide reacts with water, depending on the moisture content of the sample, to produce acetylene. As the reaction takes place in a closed environment, the increase in pressure inside the container is directly proportional to the quantity of water. The pressure is then measured by a manometer, which directly provides the moisture content on a graduated scale through correlation relations. Together with the gravimetric method (thermobalance), the carbide hygrometer is the only “direct” test that can provide a quantitative indication of the water content of a solid.
Reference standards: UNI 11121:2004; ASTM D4944-18; AASHTO T217.
