

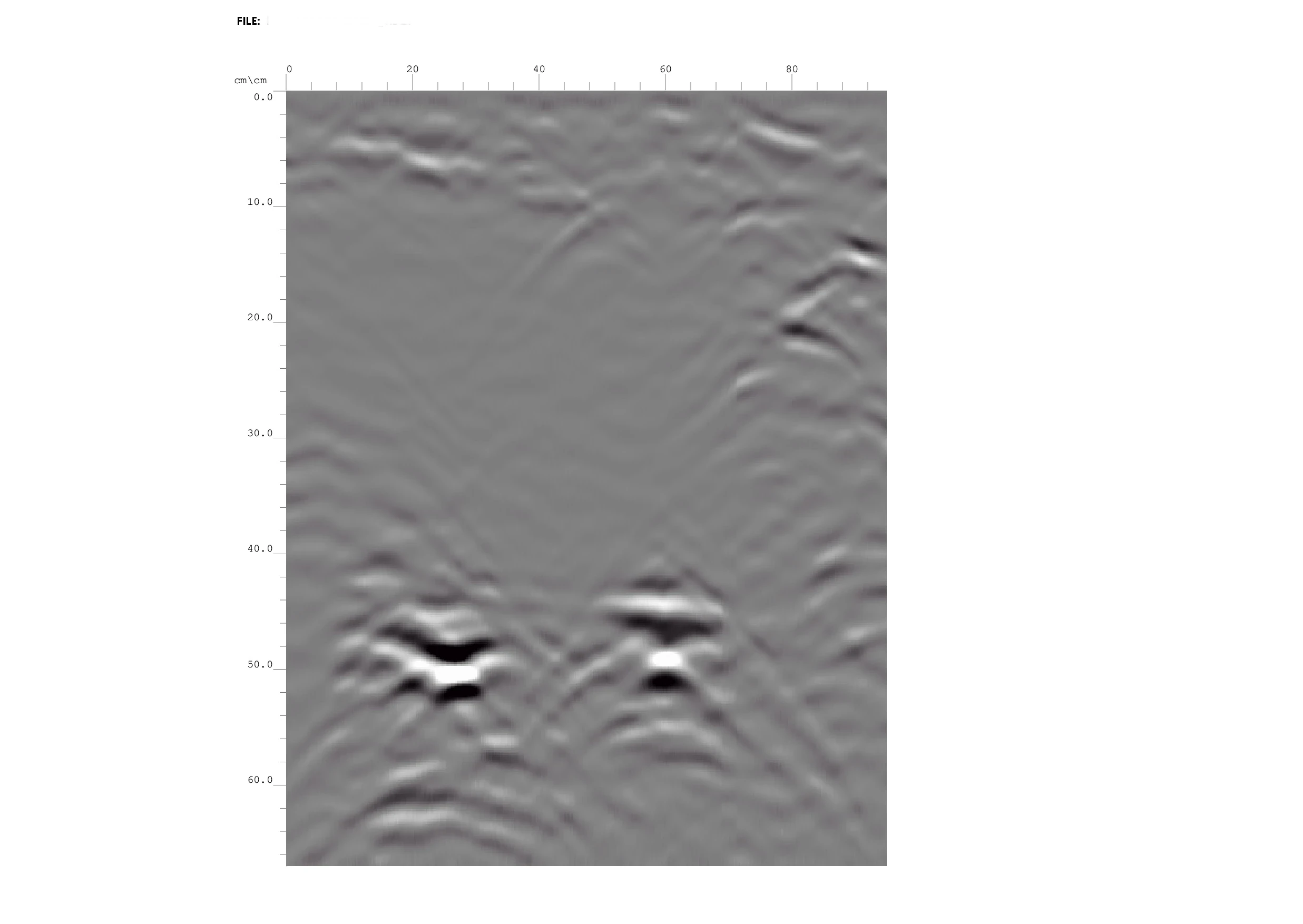
Ground Penetrating Radar survey
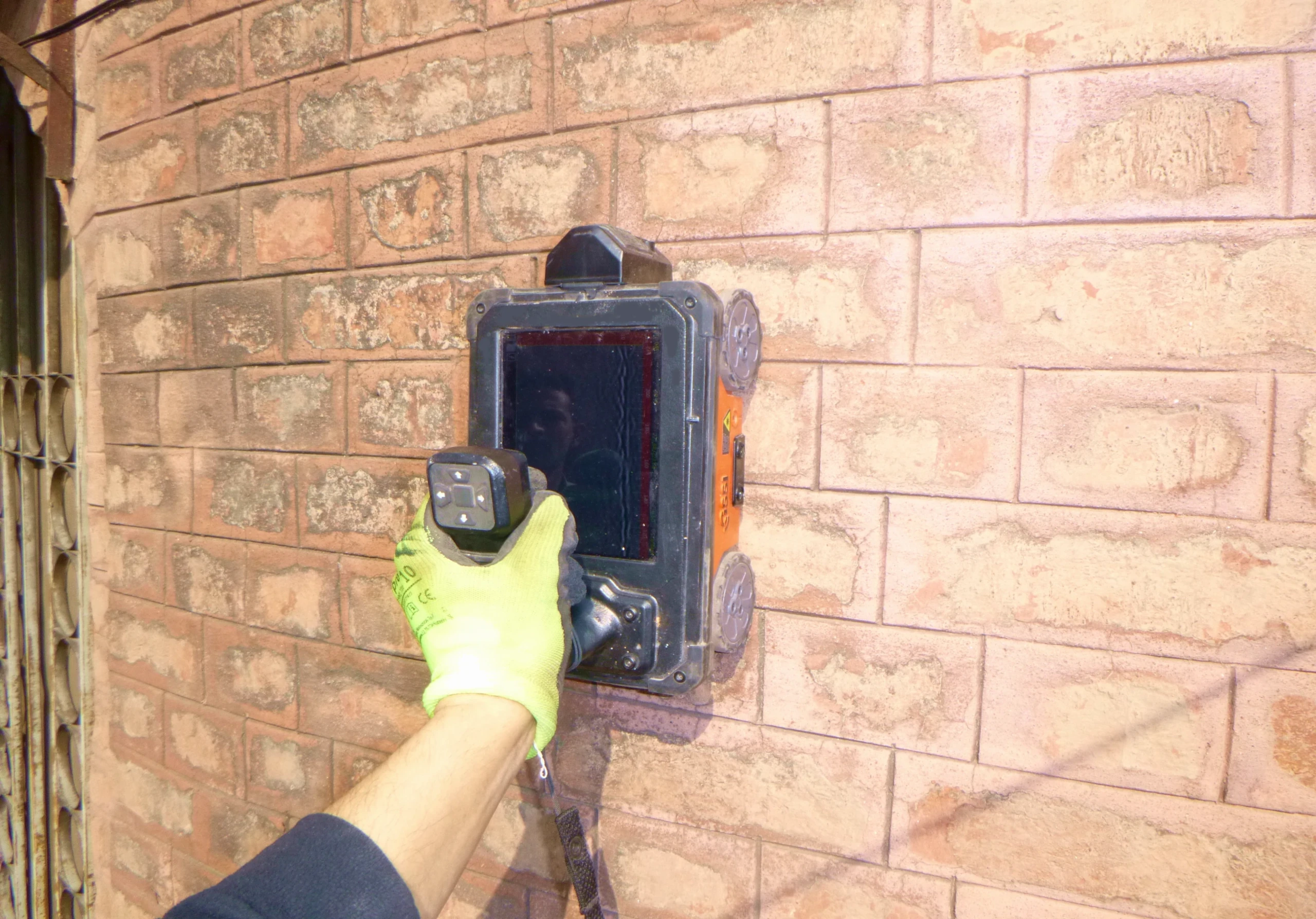
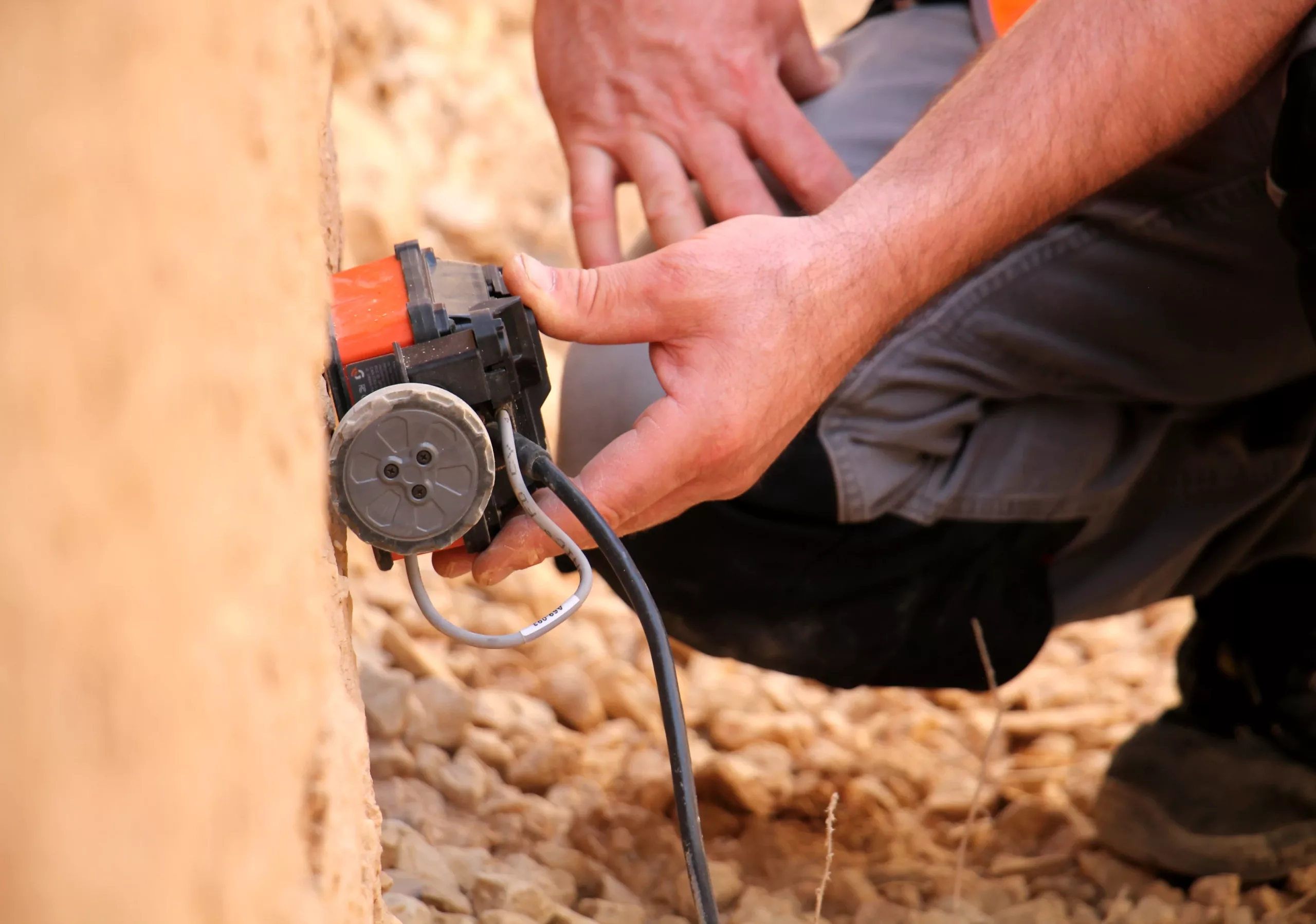
High frequency radar or GPR – Ground Penetrating Radar – survey is carried out for the identification of irregularities or anomalies within a structural element. This geophysical investigation method is based on the propagation and reflection of high frequency electromagnetic waves (range 10 MHz – 3 GHz), emitted by a transmitting antenna and detected by a receiving antenna. The electromagnetic energy is introduced into the system in the form of pulses and propagates, depending on the electromagnetic properties of the medium encountered, until it is reflected at the interfaces between media of different electromagnetic impedance (e.g. metal objects, cavities or interfaces between different materials). The reflected signal is then recorded by a receiving antenna. The speed of propagation of electromagnetic waves depends on the dielectric constant of the medium through which they pass. In the case of ground probing, lower frequency electromagnetic waves (10-400 MHz) must be introduced into the ground to achieve greater penetration.
The signal is generally transmitted and received along longitudinal paths (stripes) or with pre-defined grid for the acquisitions, using frequencies and sampling times suitable to achieve the best definition and depth in relation to the objectives to be investigated. At the end of the survey, the data are processed using appropriate software, including transmission, interpretation and graphical display with radargrams.
Reference standards: RILEM TC 127-MS.D.3; ASTM D6432-19.
